On February 15th, 2024, Professor XIAO Bin's team from the College of Pharmacy at Chongqing Medical University, in collaboration with the Department of Urology at the Southwest Hospital of the Army Medical University and the Department of Pharmacy at the Chongqing University Cancer Hospital, published a research paper in the prestigious international journal Molecular Cancer. The paper is titled "A novel peptide PDHK1-241aa encoded by circPDHK1 promotes ccRCC progression via interacting with PPP1CA to inhibit AKT dephosphorylation and activate the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway".

Clear cell renal carcinoma (ccRCC) is a prevalent malignant tumor of the urinary system, characterized by a high recurrence rate post-surgery. Patients with advanced ccRCC do not exhibit favorable responses to targeted therapies, resulting in poor longterm prognosis. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a subtype of non-coding RNAs found universally in eukaryotes. Numerous studies indicate that, contrary to the conventional definition of "non-coding" RNAs, circRNAs may serve as a template for translating proteins or peptides, presenting a novel insight and hotspot in the exploration of circRNA’s function.
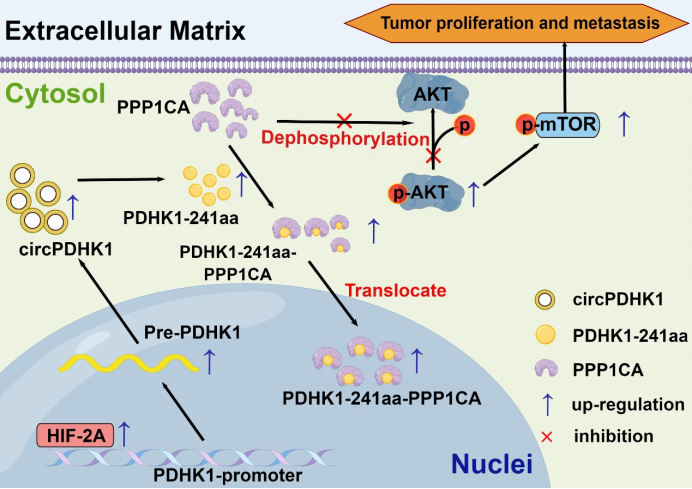
In this study, researchers conducted a systematic screening of differentially expressed circRNAs in ccRCC, and identified a novel circRNA, called circPDHK1. This circRNA was found to be significantly overexpressed in ccRCC and is closely associated with the stage, grade, and metastasis of the cancer patients. Research has established that circPDHK1 possesses the capability to be translated and encodes a novel protein, PDHK1-241aa. This study offers a fresh perspective on unraveling the mechanisms behind the development and spread of ccRCC, while also presenting a novel target for the creation of biotechnological therapeutics to treat ccRCC.
Link to full article:
https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12943-024-01940-0