On November 18, 2024, a research paper titled “Meningeal Neutrophil Immune Signaling Influences Behavioral Adaptation Following Threat” was published in the renowned journal Neuron. The study was conducted by Dr. DONG Zhifang’s team from the Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, in collaboration with Prof. REN Chunguang’s team from the College of Basic Medical Sciences. The paper unveils a neural-immune circuit involved in emotion regulation, mediated by neutrophils.

The study focuses on meningeal neutrophils, cells located in the protective layers of the brain, which are capable of responding to social threats and regulating psychological and behavioral processes. By uncovering the key role of meningeal neutrophils in perceiving social threats and modulating behavioral adaptation, this research offers new insights into the field of neuroimmunology.
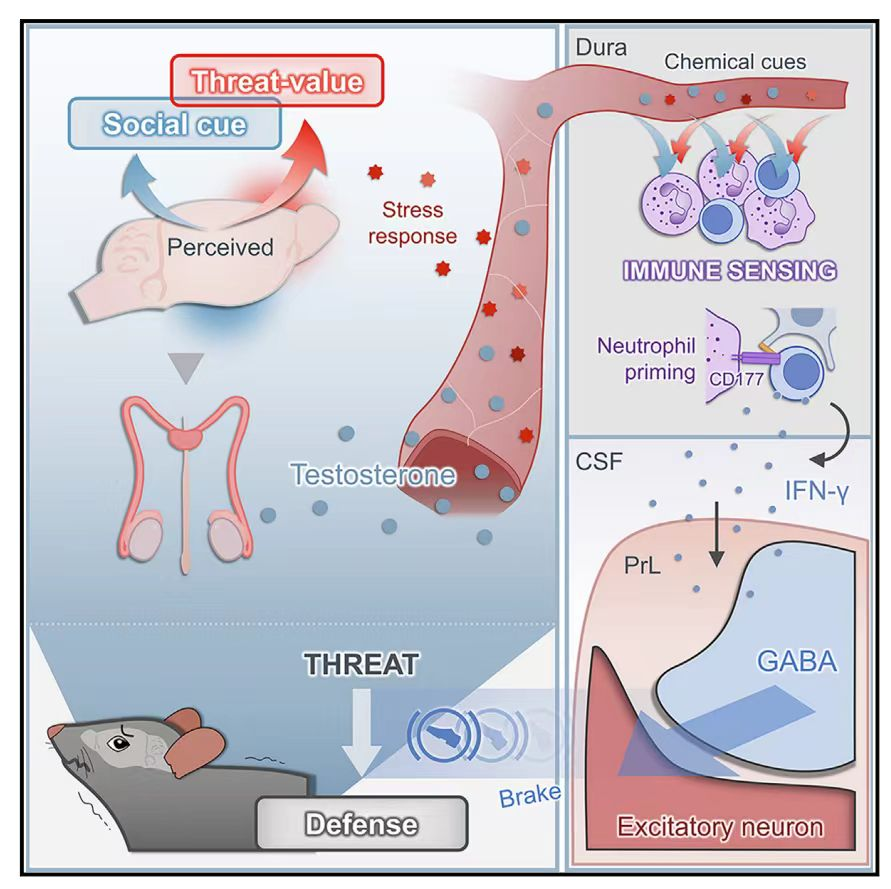
This study not only enhances our understanding of how the brain integrates immune signals to respond to social cues but also provides a foundation for the development of new therapies for emotional and behavioral disorders. As research in this area progresses, it is hoped that further exploration will unlock more secrets about the complex interactions between the brain, the immune system, and social behavior.